Due to technology in metal fabrication innovative materials with unique properties and applications have come to life, such as perforated and decoupled metals, it is crucial to understand the differences between decoupled and perforated metal as it affects selecting the right material for projects in industrial and architectural context.
Let's go deeper and compare the two materials in terms of design, properties, and uses.
Decoupled metal can be found in an engineering context and can be made by Sorting out the layers of metal in order to improve its ability to provide thermal insulation, resilence, and vibration damping. This procedure is used specifically in industries with special needs like aerospace and automotive where a reduction in weight and enhancement of energy absorption are paramount issues.
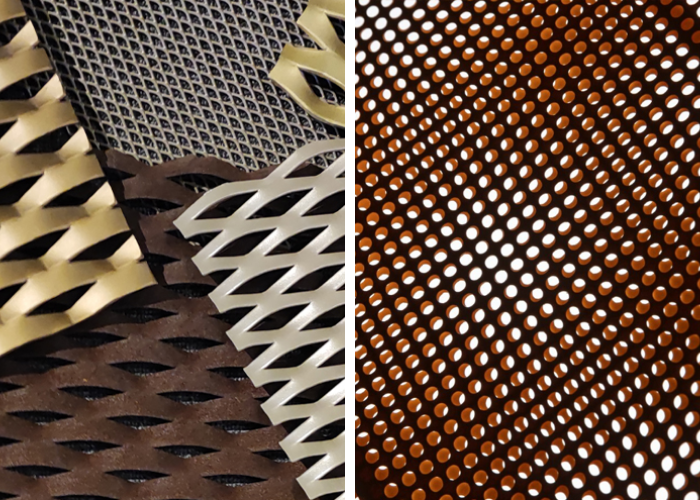
The decoupled metal properties are unavoidable for the aforementioned industries as they can be of superiority in terms of acoustic insulation and can greatly enhance absorpation of shocks that might occur, so it is a perfect selection for many applications since noise and vibration control can be greatly controlled.
İt is a durable and versatile material and to compare, decoupled and perforated durability are obviously different in many terms, for example decoupled metal surely stands out from the crowd as it performs well in noise reduction and can be of high structural adaptability and they provide exposure directly to external environmental factors such as debris and weather.
Perforated metal, as known, it is simply made by applying punching to metal surfaces leading to having holes in a wide variety of patterns and designs as a result those metal sheets can be unique aesthetically and beneficial functionally.
Perforated metal sheets are mainly used in construction to support solidity and structure they can greatly be applied to facades, ventilation grilles, sunshades and even balustrades, its ability to combine structural robustness with appealing decorativeness has made it distintc among other types of metal particularly in contemporary architecture.
We can consider perforated metal in architecture as an invitable element due to its ability to provide adequate airflow and light control maintaining the whole building design and providing an aesthetically sleek look.
Compared to decoupled metal, perforated metal enjoys versatility in the context of modern uses, ranging from acoustic panels, façade cladding, and even filtration systems. As they are characterized by perforations this allows for customized designs to meet every single specific need for various projects visually and technically.
Durability varies depending on the application when we compare decoupled metal to perforated metal, perforated metal is usually superior in outdoor environments because it can be created out of corrosion-resistant materials like aluminum or stainless steel, which can greatly ensure longevity in harsh weather. Conversely, decoupled metal is better in terms of interior applications or specialized machinery as it enjoys flexibility and can be of great energy-absorbing properties.
How to select between these materials will hugely depend on your project requirements. For facades, ceilings, or filtration perforated metal sheet is the best for those applications, moreover, perforated metal in an architectural context can offer sustainability and design flexibility but if you opt for vibration dampening or acoustic insulation decoupled metal properties should be your option to suit your needs.
For construction, automotive, and design we should clearly understand the differences between decoupled and perforated metal to ensure that we can have optimal performance and cost efficiency over time. You can make the right choice that meets your specific needs after carefully evaluating the modern uses of perforated metal and the benefits of decoupled metal.